Voyage dans la Lune, Le |
     • Directed by: Georges Méliès. • Starring: Victor André, Bleuette Bernon, Brunnet, Jehanne d'Alcy, Henri Delannoy, Delpierre, Farjaux, Kelm, François Lallement, Jules-Eugène Legris, Georges Méliès. • Music by: Jean-Benoît Dunckel, Nicolas Godin, Octavio Vázquez. • Directed by: Georges Méliès. • Starring: Victor André, Bleuette Bernon, Brunnet, Jehanne d'Alcy, Henri Delannoy, Delpierre, Farjaux, Kelm, François Lallement, Jules-Eugène Legris, Georges Méliès. • Music by: Jean-Benoît Dunckel, Nicolas Godin, Octavio Vázquez.      An association of astronomers has convened to listen to the plan of Professor Barbenfouillis, their president, to fly to the moon. With the one dissenting voice quashed by Barbenfouillis and the other members, the plan is approved with Barbenfouillis choosing five others to accompany him. Most of the preparation for the trip is in building the vessel and launching mechanism, which resemble a large bullet and a large gun respectively. Hitting the moon in the eye, the six land safely at their destination. They find that much about the moon is wonderful and fantastical, but also that much is not what they would have liked to encounter as it is life threatening. They have to find a way to get out of their alien predicament to get back home safely. An association of astronomers has convened to listen to the plan of Professor Barbenfouillis, their president, to fly to the moon. With the one dissenting voice quashed by Barbenfouillis and the other members, the plan is approved with Barbenfouillis choosing five others to accompany him. Most of the preparation for the trip is in building the vessel and launching mechanism, which resemble a large bullet and a large gun respectively. Hitting the moon in the eye, the six land safely at their destination. They find that much about the moon is wonderful and fantastical, but also that much is not what they would have liked to encounter as it is life threatening. They have to find a way to get out of their alien predicament to get back home safely.
|
Review:




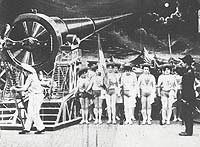


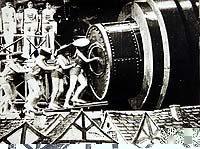



Méliès used the stop-motion (or substitution-splice) effect and arising smoke for explosive characters in many of his films--same with superimpositions, animated miniatures and placing a fish tank in front of the camera. Additionally, his set designs were the best of the day. I easily forget it's all done within a cramped studio. He often used moving props, too, but this is one of the few that I've seen where the prop is pulled towards the camera--creating the famous rocket kissing the moon's eye gag. The following shot is a temporal replay of that action from a different perspective. It works here, but Edwin S. Porter would make the mistake of adopting the technique for "Life of an American Fireman", which was reedited later, leading many to believe it was a landmark in narrative editing. The "30 tableaux", as Méliès called it, is linked by dissolves--a common transition at the time, which he introduced.
Méliès made it known that his goal was to push cinema towards resembling theatre. The benefit was longer films with more developed stories. Given this, it's ironic that he was one of the first filmmakers to achieve effects specific to motion pictures (i.e. incapable of being produced in theatre or other art forms)... i.e. the trick shots.
Numerous early shorts are blatant imitations of Méliès's work, but they usually weren't as funny or creative. Many studios even duped his films and sold them as their own, which led to Méliès patenting his work in the U.S. and joining the Motion Pictures Patents Company (MPPC). "A Trip to the Moon" represents the height of his career. His work would soon diminish under the hectic schedule of the Nickelodeon age and the monopolization by the MPPC and Pathé, and he would end up burning his own negatives. Watch Jacques Meny's documentary "La Magie Méliès" (1997) for a good telling of his life and films.
(Note: This is one of four films that I've commented on because they're landmarks of early narrative development in film history. The others are "As Seen Through a Telescope", "The Great Train Robbery" and "Rescued by Rover".).
Review by Cineanalyst from the Internet Movie Database.
Movie Database
